Cases of cybercrime and phishing have been steadily rising over the last few years, and unfortunately the Covid-19 pandemic is making things significantly worse. The FBI reported that as of April 2020, instances of cybercrime have risen by 300% since the beginning of the pandemic.
With ever more people working online, it’s more important than ever that every netizen learns how to protect themselves, and what to be on the lookout for. Here are 10 signs of trustworthy websites that you can use to ensure they are legitimate.

1. HTTPS
If a website URL starts with HTTPS (rather than just HTTP) this means the site encrypts data requests and responses. In plain language, this makes it harder for a malicious third party to steal your information. This is especially important if you intend to make some kind of purchase on the website. Never enter your payment or credit card details into an HTTP site!
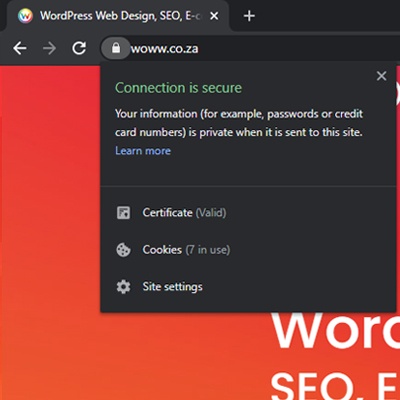
2. Security status and padlock icon
Your browser also has built-in tools to help keep you safe. Check for the small padlock icon to the left of the URL, and always take heed if your browser warns you against a particular site.
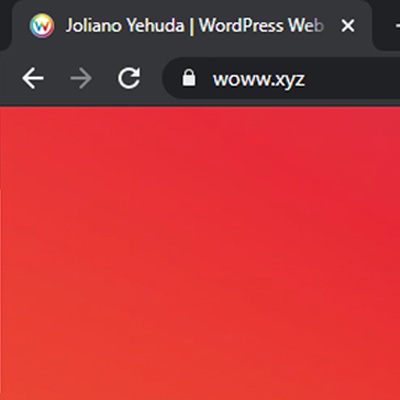
3. Double check the spelling of the URL
Cyber criminals are getting extremely crafty, and sometimes an illegitimate website is practically indistinguishable from the real thing, at least in look and design. One particularly sneaky tactic is to disguise the site’s actual domain with a slightly longer address, for example:
www.yourbank.com.abcd123.actualdomain.com
At first glance, the domain looks legit – yourbank.com – but that’s not actually the real domain you’re visiting, is it? Be especially cautious if you’ve followed a link in an email to get to the site.
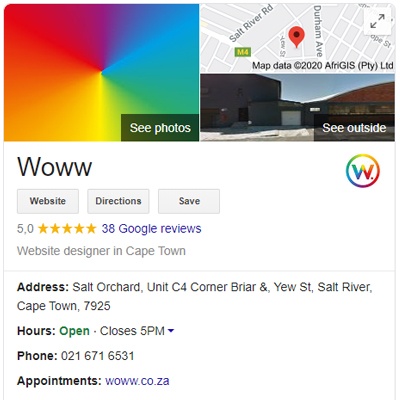
4. Look for positive reviews and testimonials
If you haven’t used a service before, take a few minutes to check whether the website has some good reviews online. Don’t let yourself fall into the same trap as previous victims when they’ve taken the time to warn others of a dodgy platform.

5. Follow the trust seals
If a website works with a variety of payment or software providers (major credit card companies, the Google Play Store, PayPal, etc) then they should display trust seals from these companies, normally in the website footer. Don’t take their word for it though! You’ll find you can actually click on these trust seals and see the website’s certificate from the provider. If you can’t click on them, then the site owner has simply pasted images of the seals – a big red flag.
6. Decent spelling and grammar
A legitimate business is going to spend the time and money making sure their website reads well and isn’t full of spelling and grammar mistakes. Someone out to scam you probably isn’t going to bother.

7. Google the URL
If you can’t tell whether a website is legit or not, then there’s a really simple way to put your mind at ease. Simply copy the URL and Google it! Google provides a service called the Google Safe Browsing Transparency Report, which will warn users if the site they’ve searched for can’t be trusted. Best of all it will take you mere seconds.

8. Check for a privacy policy
A privacy policy outlines how a website goes about protecting their users’ data, as well as what information they collect and store, for how long, and why. You can usually find a link to this page on the website’s footer. Websites without privacy policies either don’t want you to know what they’re doing with your data, or simply haven’t bothered to help you feel secure.

9. Site not overcrowded with intrusive adverts
Lots of websites have a few adverts here and there to bring in extra revenue – and there’s nothing wrong with that. However, when a website is swamped with dozens of them and they actually make it hard to navigate around, that’s a fairly good sign they’re not interested in helping their visitors, but rather making a quick buck off them.
10. Verifiable contact information available
A legitimate company should have no problem with their customers getting in touch, or knowing where they’re located. If all that’s offered is a contact form, that’s a warning sign they may not be who they claim. If an address is given, do a quick online search to verify it matches up with the company name.
All these measures might sound a little extreme, but the unfortunate reality is that phishing scams and cyber criminals are getting more and more sophisticated – and ambitious. The better you know how to protect yourself and what to be on the lookout for, the less likely you are to fall victim to them.